Company’s ecological footprint
Ecological footprint method enables to evaluate the environmental impact of the activities of companies and states in a complex manner. The basis for the calculation of ecological footprint is land as a limited resource used by people for their needs.
Ecological footprint is a measure of human demand for the use of natural resources for their activities. Ecological footprint assesses the use of space accompanying the lifecycle of a product or service and can be measured in hectares per year (hereinafter ha per year). The Ecological Footprint Index demonstrates how much water and productive land is occupied for producing, using and absorbing materials to be consumed.
The calculation of a company’s ecological footprint is based on two simple facts:
- It is possible to monitor and detect the majority of the resources consumed by the company and several additional outputs;
- It is possible to measure the majority of the resources and waste flows in terms of biologically productive area which is required for producing these resources and for disposing and neutralizing waste.1
Ecological footprint factor is a conversion unit which helps to equalize the measured source data so that the result would be easily understandable and comparable.
Environmental impact measured on the basis of the ecological footprint method
Ecological footprint is calculated based on the methodology developed by the Estonian Fund for Nature. The calculation takes into consideration 11 different components and corresponding factors. The components have been divided into five fields (water, waste, electricity, heating, transport). In order to get a better comparison, the ecological footprint per one employee has been pointed out separately.
It must be emphasized that it is fair to compare the ecological footprints per person of various companies only in case the companies provide similar products or services and the ecological footprint has been calculated for the same indicators.
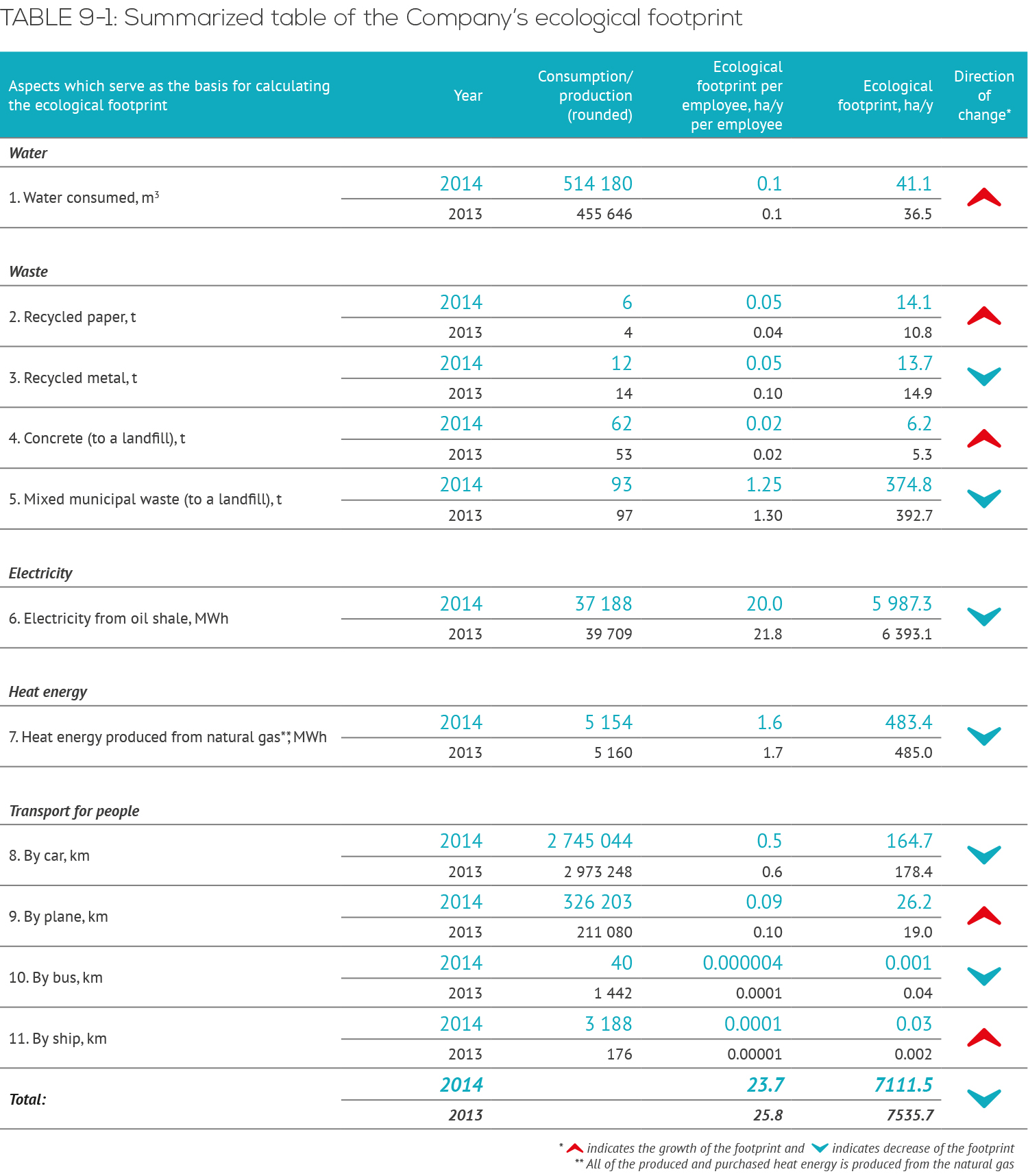
Summarized table of the Company’s ecological footprint
Annually, the Company has the strongest impact on the environment through its use of electricity, followed by the use of heat energy and waste production. The use of electricity and heat energy are in a close and inevitable connection with the Company’s core activity and with the expansion of the activities also the ecological footprint inevitably increases. Efficient and sustainable use of electricity and heat energy was one of the priorities in 2014. Consequently, the ecological footprint caused by the use of electricity and heat energy has decreased and thus positively affected the total ecological footprint of the company. Table 9-1 presents the size of footprints caused by the consumption of various ecological footprint components. We will have a closer look on the consumption of all resources in the following chapters of the report.
1 Ecological Footprint of Nations
2 Ecological footprint factors were taken from Chambers et al, Sharing Nature`s Interest, 2000 (available in ELF library)